The image magnification,
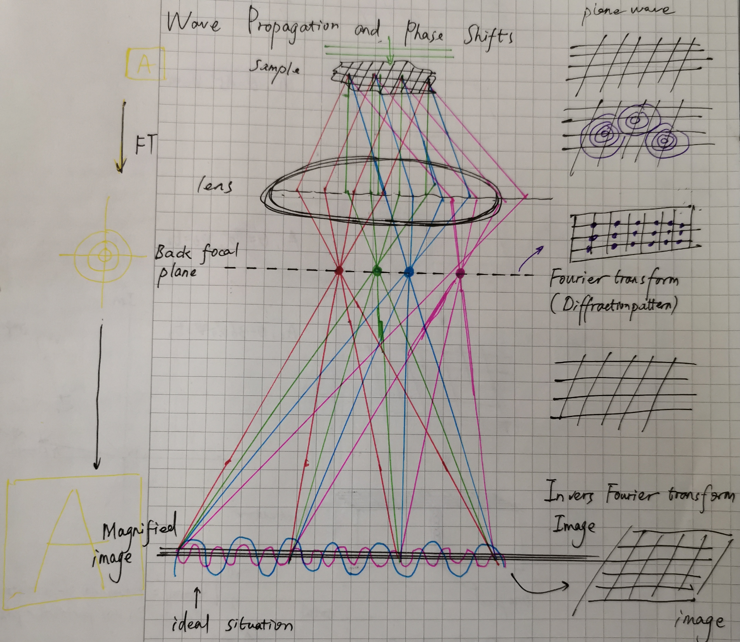
as seen in the figure, when the scattered electrons poass through the lens which will get together at the imaginary back focal plane, which is just like the fourier transform process, and when pass into the detector, just like the inverse fourier transform which will give a magnified image.
But, not all of the components in the image appear equally stong, some of the fourier components are represented fully in the final image, other may only half of they should be, some are entirely missing.
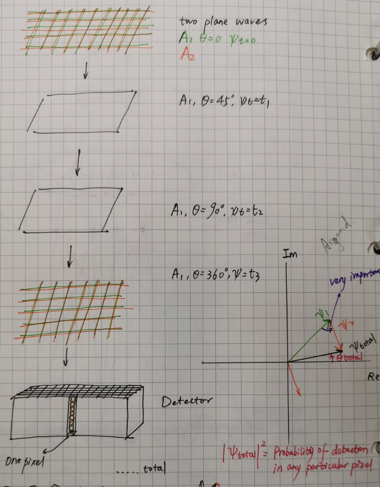
This figure gives why some information will miss out. When there is only one plane wave with amplitude $A_1$, at different phases (θ) will give different Ψ, and
$|ψ_{total}|^2=$ Probability of detection in any particular pixel
In the argand, we get get a round circle to show this.
Now imaginate the situation of two plane waves which is more similar to the real situation. At the argand, we will get the total phase and the intersection angle (α) which will help us understand why some are missing.
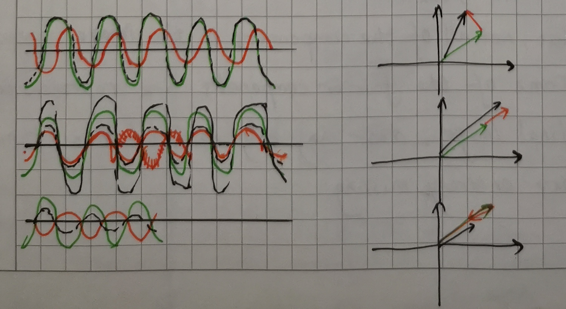
From the figure, we can see, if the α is 90°, the total wave is similar to the green wave and this will make information missing.